DYNAMIC VOLTAGE RESTORER
Introduction
Dynamic voltage skilled worker (DVR) may be a series-connected versatile ac transmission systems (FACTS) controller wont to compensate voltage sags and swells throughout abnormal conditions in distribution systems. There ar totally different system topologies of the DVR, that are evaluated andhierarchical . Four totally different system topologies for DVR are analyzed and tested with target the tactic wont to acquire the mandatory energy throughout voltage sags. 2 topologies take energy from the grid and therefore the different 2 topologies take energy from the energy storage devicesthroughout the voltage sag. These topologies are: (i) DVR with no storage and supply-side connected shunt device, (ii) DVR with no storage and load-side-connected shunt device, (iii) DVR with energy storage with variable dc-link-voltage and (iv) DVR with energy storage and with constant-dc link voltage. Experimental and simulations are performed to rank these topologies reckoning on the specifiedperformance and price of the DVR. Overall analysis has shown that topology range a pair of has the best score.
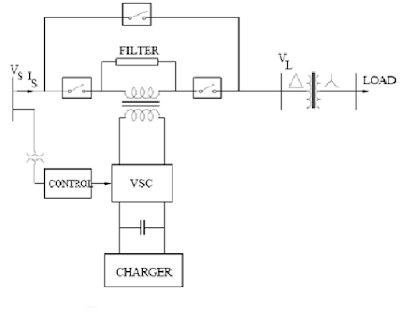
Voltage Source Converter(V.S.C):
This could be a three section - three wire VSC or three section - four wire VSC. The latter permits the injection of zero-sequence voltages. Either a traditional 2 level device (Graetz Bridge) or a 3 leveldevice is employed
Boost or Injection Transformers:
Three single section transformers ar connected nonparallel with the distribution feeder to couple the VSC (at the lower voltage level) to the upper distribution voltage level. The 3 single transformers will beconnected with star/open star winding or delta/open star winding. The latter doesn't allow the injection of the zero sequence voltage. the selection of the injection electrical device winding depends on the connections of the step down trans- former that feeds the load. If a ¢ ¡ Y connected electrical device (as shown in Fig. 3) is used, there's no got to compensate the zero sequence voltages.
However if Y ¡ Y reference to neutral grounding is employed, the zero sequence voltage might have to be compelled to be remunerated. it's essential to avoid the saturation within the injection transformers.
Passive Filters:
The passive filters will be placed either on the high voltage aspect or the device aspect of the boost transformers. the benefits of the device aspect filters ar (a) the parts ar rated at lower voltage and (b) higher order harmonic currents (due to the VSC) don't °own through the electrical device windings. The disadvantages ar that the filter inductance causes drop and section (angle) shift within the(fundamental element of) voltage injected. this may erect the management theme of DVR. the placement of the filter o the high voltage aspect overcomes the drawbacks (the discharge electrical phenomenon of the electrical device will be used as a filter inductor), however leads to higher ratings of the transformers as high frequency currents will flow through the windings.
Energy Storage:
This is needed to produce active power to the load throughout deep voltage sags. Lead-acid batteries,regulator or SMES will be used for energy storage. it's conjointly potential provide|to produce} the specified power on the DC aspect of the VSC by associate degree auxiliary bridge device that's fed from associate degree auxiliary AC supply
benefits of DVR:
The major objectives ar to extend the capability utilization of distribution feeders (by minimizing the rms values of the road currents for a such that power demand), cut back the losses and improve power quality at the load bus. the main assumption was to neglect the variations within the supply voltages. This primarily implies that the dynamics of the supply voltage is far slower than the load dynamics.
When the quick variations within the supply voltage can't be neglected, these will erect the performance of essential hundreds like (a) semiconductor fabrication plants (b) paper mills (c) foodprocess plants and (d) automotive assembly plants. the foremost common disturbances within thesupply voltages ar the voltage sags or swells that may result to (i) disturbances arising within thegear mechanism, (ii) adjacent feeder faults and (iii) fuse or breaker operation.
Voltage sags of even 100 percent lasting for 5-10 cycles may result in pricey injury in essentialhundreds. The voltage sags will arise attributable to symmetrical or unsymmetrical faults. within thelatter case, negative and 0 sequence parts are gift. unpaid nonlinear hundreds within the distribution system will cause harmonic parts within the offer voltages.
To mitigate the issues caused by poor quality of power offer, series connected compensators ar used. These ar known as as Dynamic Voltage skilled worker (DVR) within the literature as their primary application is to complete voltage sags and swells. Their configuration is comparable thereto of SSSC,mentioned in chapter seven. However, the management techniques ar totally different. Also, a DVRis anticipated to retort quick (less than 1/4 cycle) and so employs PWM converters mistreatmentIGBT or IGCT devices.
D.V.R:
the primary DVR entered industrial service on the Duke grid in U.S.A. it's a rating of two MVA with 660 kJ of energy storage and is capable of compensating five hundredth voltage sag for a amount ofzero.5 second (30 cycles). it absolutely was put in to guard a extremely machine-driven yarnproducing and floor cover weaving facility.
Since then, many DVRs are put in to guard micro chip fabrication plants, paper mills etc. Typically, DVRs ar fabricated from standard style with a module rating of two MVA or five MVA. they needbeen put in in substations of voltage rating from eleven kilovolt to sixty nine kilovolt. A DVR needs tooffer energy to the load throughout the voltage sags. If a DVR needs to offer active power over longer periods, it's convenient to produce a shunt device that's connected to the DVR on the DC aspect.
As a matter of truth one might ideate a mix of DSTATCOM and DVR connected on the DC aspect tocomplete each load and provide voltage variations. during this section, we tend to discuss the appliance of DVR for harmonic voltage.
The voltage supply device is often one or a lot of converters connected nonparallel to produce the specified voltage rating. The DVR will inject a (fundamental frequency) voltage in every section ofneeded magnitude and section. The DVR has 2 operational modes.
1. Standby (also termed as contact operation (SCO) mode) wherever the voltage injected has zero magnitude.
2. Boost (when the DVR injects a needed voltage of applicable magnitude and section to revive the pre-fault load bus voltage).
The management theme has 2 management loops; the inner loop and therefore the outer loop that ar,severally, answerable for generating the gate signal of the switches of the DVR and therefore thereference voltage signal of the DVR. A DVR example has been engineered and tested with non-linear load. a unique management strategy, that has been valid mistreatment time domain simulations, for the electrical condenser supported DVR has been planned to compensate voltage sags.
The possibility of compensating harmonics mistreatment DVR at medium voltage level has been investigated. a bearing strategy has been enclosed within the main system of the DVR to compensatehand-picked harmonics throughout steady state. The topology of the used DVR relies on a dcelectrical condenser supported DVR. during this paper, a DVR with the aptitude to compensate harmonics and deep voltage sags is planned
Comments
Post a Comment