JSP Life Cycle:
A JSP life cycle can be defined as the entire process from its creation till the destruction which is similar to a servlet life cycle with an additional step which is required to compile a JSP into servlet.
Following are the steps followed by a JSP Container: ◦ Compilation
◦ Parsing the JSP.
◦ Turning the JSP into a servlet.
◦ Compiling the servlet.
◦ Initialization
◦ Execution
◦ Cleanup
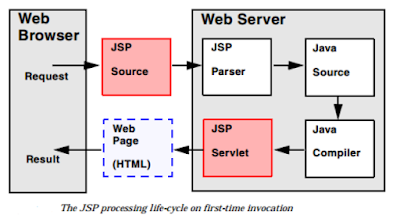
Architecture:
1. JSP Compilation: When a browser asks for a JSP, the JSP engine first checks to see whether it needs to compile the page.
If the page has never been compiled, or if the JSP has been modified since it was last compiled, the JSP engine compiles the page.
The compilation process involves three steps:
◦ Parsing the JSP.
◦ Turning the JSP into a servlet.
◦ Compiling the servlet.
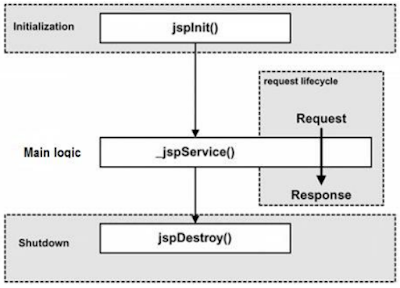
2. JSP Initialization: When a container loads a JSP it invokes the jspInit() method before servicing any requests.
If you need to perform JSP-specific initialization, override the jspInit() method:
public void jspInit(){
// Initialization code...
}
Typically initialization is performed only once and like the servlet init() method, we initialize database connections, open files, and create lookup tables in this method.
3. JSP Execution: This phase of the JSP life cycle represents all interactions with requests until the JSP is destroyed.
◦Whenever a browser requests a JSP and the page has been loaded and initialized, the JSP engine invokes the jspService() method in the JSP.
◦The jspService() method takes HttpServletRequest and HttpServletResponse as its parameters as follows:
void jspService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
{
// Service handling code...
}
The jspService() method of a JSP is invoked once per a request and is responsible for generating the response for that request and this method is also responsible for generating responses to all seven of the HTTP methods
ie. GET, HEAD, POST, DELETE, PUT, TRACE & CONNECT.
4. JSP Cleanup: The destruction phase of the JSP life cycle represents when a JSP is being removed from use by a container.
◦ The jspDestroy() method is the JSP equivalent of the destroy method for servlets.
◦Override jspDestroy() when you need to perform any cleanup, such as releasing database connections or closing open files.
◦ The jspDestroy() method has the following form
public void jspDestroy() {
// Your cleanup code goes here.
}
 |
The translated java source files and class are located in: C:\Users\srini\workspace\.metadata\.plugins\org.eclipse.wst.server.core\tmp0\work\Catal ina\localhost\JSPProject\org\apache\jsp
Comments
Post a Comment